Disruption of copper and zinc homeostasis is directly implicated in Menkes and Wilson’s disease as well as cancers and neurological diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and prion disease. Metal chelators are used in the treatment of these types of diseases. This project aims: (1) to characterize the selective chelating performance of our newly designed set of alternative metal-binding peptides (ambs) and compare them to the copper-binding peptide methanobactin (mb-OB3b) which has already shown therapeutic potential; (2) to develop ion mobility-mass spectrometry (IM-MS) techniques to study how the primary structure affects the secondary and tertiary structures, chelation reactions, and their collision-induced dissociation (CID) mechanisms; and (3) to engage undergraduate students at Texas A&M-Commerce in research that crosses the interdisciplinary boundaries.
Research Activities: The solution-phase metal ion reactivity of ambs and mb-OB3b will be examined by electrospray ionization - IM-MS and density functional theory (DFT). Ultraviolet-visible and fluorescence spectral techniques will be used to check for correlations across gas- and solution-phase analyses to answer the following questions:
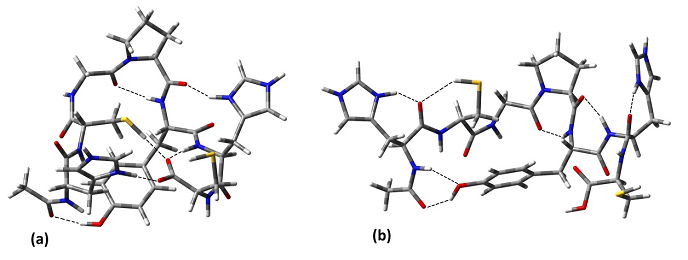
Figure 1. The lowest energy conformers located using the B3LYP/LanL2DZ method a) [amb5A+H]+ and b) [amb5A+2H]2+. The dashed lines represent the salt-bridges and hydrogen bonds that stabilize the secondary structures and include a tight turn at Pro4 augmented with a hydrogen bond between the backbone carbonyl and amine groups of Gly3 and Tyr5, and a hydrogen bond between the substituent hydroxyl group of Tyr5 and the carbonyl of the N-terminus acetyl group. The 2+ conformer exhibits the most elongated structure, because of the charge repulsion between the two protonated substituent groups of His1 and His6 which are separated by a distance of almost 14 Å. This charge repulsion is mediated in the 1+ conformer, which exhibits a folded secondary structure, due to a salt-bridge between the imidazolium of His1 and the carboxylate of the C-terminus, and a hydrogen bond between the thiol of Cys2 and the C-terminus carboxylate. The theoretical collision-cross sections (Ω) of the 2+ and 1+ conformers are 234 ± 14 Å2 and 203 ± 6 Å2, respectively, which agree with the IM-MS measurements of 220 ± 8 Å2 and 201 ± 8 Å2 (uncertainties 2σ).
The 2013 Nobel Prize in chemistry was awarded for the efforts of Martin Karplus, Michael Levitt and Arieh Warshel, who laid the foundation for the powerful computational programs that are used today to understand and predict various chemical processes. Computational chemistry is so realistic that it can very accurately predict the outcomes of traditional experiments. In the pharmaceutical industry, computation chemistry is often used to simulate how a drug couples with its target protein in the body, and predict the important interactions and hence assist with the design of new drugs. It is often said that computational modeling programs are just as important for today’s chemists as the test tube! One aspect of our research involves using computational to analyze the factors that influence the outcomes of the hetero Diels Alder reaction and to be able to predict the outcomes of these reactions. Ever since the discovery of the Diels-Alder reaction (DA), it has become a cornerstone reaction in organic chemistry for the synthesis of carbon-carbon and carbon-heteroatom bonds. Researchers over the years have been inspired to develop different catalysts to effectively catalyze these reactions. The catalytic asymmetric DA reactions have emerged as a powerful methodology for the stereoselective construction of functionalized six membered rings with control of regio-, diastereo-, and enantioselectivity. The inverse-electron demand hetero DA (HDA) reactions, which involve the incorporation of heteroatoms, such as oxygen or nitrogen, have given rise to the construction of heterocyclic compounds that are of extreme importance in medicinal chemistry. A major advantage of using the HDA reactions for the synthesis of such compounds is the facile stereospecific introduction of functionalized ring systems with up to four stereocenters in the products.
We have recently studied the effectiveness of a series of proline substituted derived organocatalysts in promoting the enantioselective outcomes of the HDA reactions of aldehydes with electron-deficient enones.
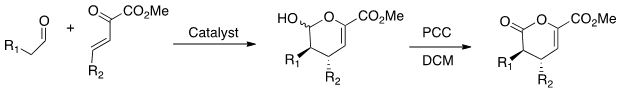
Our research uses computational calculations to predict the outcomes of these reactions. The first phase of this project uses computational calculations to analyze the transition state for the model reaction below.
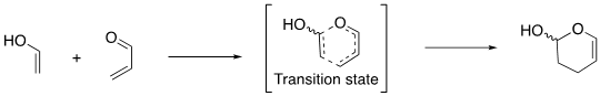
After gaining an understanding of the factors that affect the stability of the transition state for these reaction types, we will utilize the reaction shown below to investigate the effects of different substituents on the diene and dienophile on the regio-, diastereo-, and enantioselectivities of the products.

The results obtained via these calculations will be matched against experimental results in order to develop a computational model to predict the outcome of the hetero Diels Alder reactions.
Dr. Jang’s recent research effort includes two main projects. The 1st project focuses on the investigation of the properties of catalysts for selective hydrogenation, including in both liquid and gas phases. It is our goal to develop and design a more efficient catalyst, with high activity and selectivity and good stability, for selective hydrogenation of compounds in industrial processes, such as multi-billion dollar polyethylene industry. Novel procedures and treatment processes are applied to metal and/or metal oxide catalysts to obtain novel catalytic materials. Characterizations of catalysts prepared by impregnation, precipitation, ion exchange, and others were routinely carried out by various instrumentation techniques, such as DSC (Differential Scanning Calorimetry), in situ FT-IR (Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy), chemisorption, temperature programmed adsorption/desorption, etc.
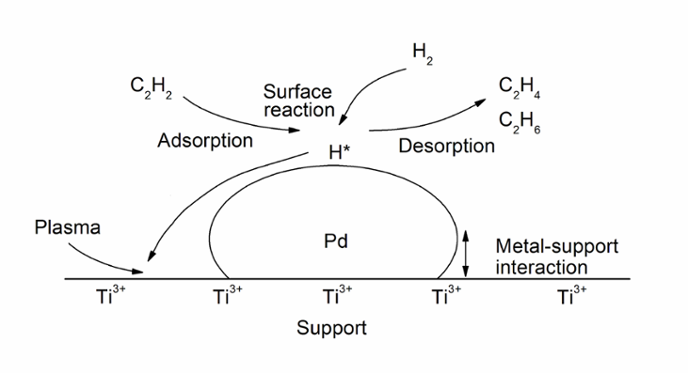
Although any reaction on catalyst surface is complicated, the selective hydrogenation of acetylene can be shown schematically in the figure below, including adsorption, surface reaction and desorption while catalyst properties could be changed by various procedures, such as reduction, oxidation, plasma, etc.
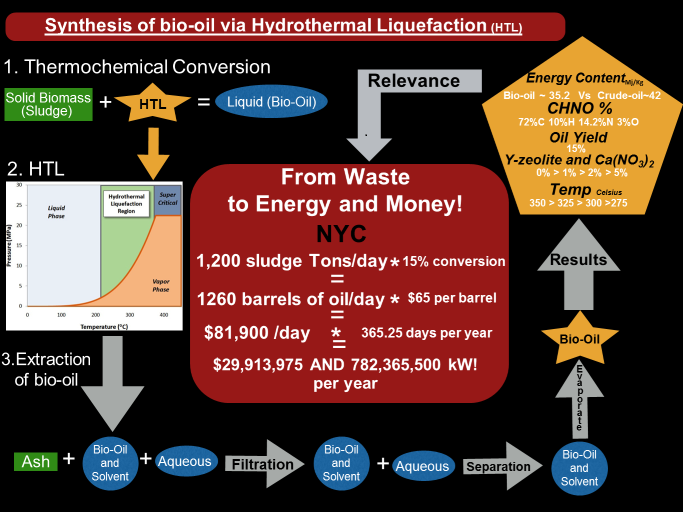
Another project focuses on bio-oil production from biomass and wastes via hydrothermal liquefaction (HTL) and the upgrade of bio-oil with catalysts and/or alcohols. The objective is to produce renewable energy while taking care of the environmental issues. For bio-oil production, biomass (such as algae) or wastes (such as sludge) will go through HTL processes followed by separation, extraction, identification and quantification to characterize the content and composition of the bio-oils. The benefits of the project could be visualized from the schematic diagram in the figure below which calculates the revenue could be generated by converting the sludge produced in New York City per year to bio-oil.
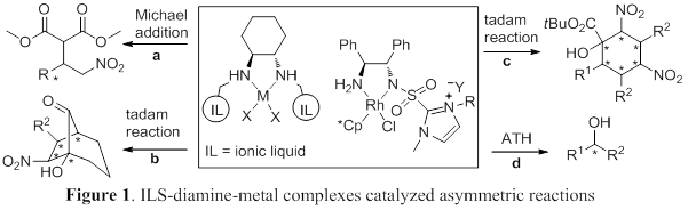
The objective of my research projects is to develop novel chiral diamine ligands and their application for transition metal catalyzed asymmetric reactions. Due to the high demand and preference for the use of enantiopure compounds in the fields of pharmaceuticals, perfumes, food additives, etc., there has been a great interest in catalytic asymmetric synthesis as a tool for their efficient preparation. However, it has been a big challenge to obtain optically active compounds with good yields and selectivities. In the first phase of these projects, we will build on the knowledge gained from our previous work and design, synthesize and characterize various chiral diamines. In the second phase, the ability of the resulting chiral diamines as ligands for transition metals Ru, Cu, and Ni catalyzed asymmetric reactions will be carried out using selected asymmetric reactions such as Michael reaction, asymmetric transfer hydrogenation, and tandem reactions (Figure 1). Also, the extractive electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (EESI-MS) analysis will be carried out to elucidate the structural information about the reaction intermediates and the coordination chemistry of diamine ligand with transition metal in order to better understand their influence on the asymmetric controls and to assist in optimizing their structures to give more effective chiral diamines. The knowledge gained will provide fundamental insights to better understand the mechanism of asymmetric induction for a wide range of reactions.
There are 3 main projects in the Starnes research group.
Project 1: The Development of Synthetic Hosts for Anion Recognition Applications.
One aspect of the Starnes research group is centered on the development of synthetic receptors for anions of environmental and biological significance. Environmentally, many anions (such as perchlorate, nitrate, nitrite, sulfate and pertechnetate) present themselves as toxic and problematic contaminants in lakes, rivers, aquifers, nuclear waste repositories etc. We aim to develop sensors and extraction agents for these anions. There are also many anions of biological importance such as DNA, RNA, proteins and peptides. The development of receptors for these analytes has diagnostic applications in the monitoring of cellular processes.
The research utilizes computational software to design the artificial receptor on a computer, analyze its conformational preferences computationally and then evaluate the receptors molecular recognition properties computationally. Receptors showing promise computationally are then synthesized in lab and studied for their anion recognition properties.
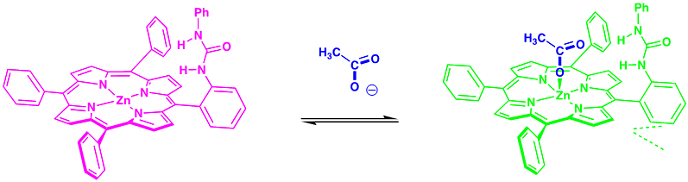
Representative example of anion recognition
Project 2: The Development of Synthetic Hosts for Chiral Recognition Applications.
The research group is working to modify hosts previously prepared in the research group that have been shown to function as stereoselective hosts for chiral guests in order to 1. improve on the selectivity of these types of hosts in their guest binding properties and 2. to learn more about the conformations of the hosts and host-guest complexes which will allow the group to improve on host design. One practical result from the work is that it will lead to a better understanding of biological chemistry. Chiral compounds are important, especially in biological chemistry. For example, one enantiomer of a chiral drug is useful whereas its enantiomer might be toxic or deadly. Many biological substrates and structures are chiral as well (such as proteins and what they act on or the product of an enzyme catalyzed reaction). By understanding chiral recognition better, we can understand biological chemistry better or biological recognition in general better. Understanding the structures of the hosts and their complexes will contribute to a better understanding of the requirements for selective chiral recognition. The research could also impact the design of sensors for chiral species, the development of catalysts for chiral synthesis and the separations industry (for the separation of chiral substances such as enantiomeric molecules, which would greatly impact the pharmaceutical industry since one enantiomeric of a chiral drug might be toxic and therefore must be isolated and removed from the drug mixture).
Project 3: The Development of Molecular Switches. A molecular switch is a molecule or set of molecules that will undergo a pre-defined shift between two or more distinct states in response to a specific stimuli. A schematic illustrating the basic concept is below. There is interest in the development of molecular switches for a variety of applications such as in nanotechnology for application in molecular computers (the different states can represent the binary numerical system 0 and 1).
For this project, we will develop synthetic host compounds that contain a mechanism for a switching stimuli that arises from the stereochemistry (3D shape) of a guest which binds to the host. Depending on the absolute stereochemistry of the guest, the host will exist in one of two different conformations; if the host can exist in conformer A and conformer B, when one enantiomer of a guest binds to the porphyrin host, the host will adopt conformer A. When the opposite enantiomer of a guest binds to the host, the host will adopt conformer B. We aim to utilize 19F-NMR, Circular Dichroism (CD), and fluorescence spectroscopy to determine which conformer the host exists in (and hence determine which stereoisomer of guest is bound). If successful, we will be able to determine the absolute stereochemistry of a guest or the stereocomposition of a mixture of enantiomers from the 19F-NMR, CD or fluorescence response. This will represent a major advance is chiral discrimination using spectroscopic methods. The knowledge gained from this study will contribute to a better understanding of the requirements for selective chiral recognition. This type of system could find use in the pharmaceutical industry for example for high-throughput enantiopurity determination of chiral pharmaceutical agents.

A student working on any of these projects will be trained in synthetic organic chemistry, including the synthesis, isolation, purification and identification of organic compounds. The student will use techniques such as computational chemistry, NMR, IR, circular dichroism, fluorescence and mass spectrometry to study the systems.
The basic area of my research program has focused on examining the regulation of nucleic acid metabolism from an evolutionary perspective. My laboratory has been investigating the control of pyrimidine biosynthesis in pseudomonads relative to their evolving taxonomy. Pyrimidine biosynthesis is essential to prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells as it provides the substrates (UTP, CTP, dCTP and dTTP) necessary for the synthesis of RNA and DNA. There are six de novo pyrimidine biosynthetic enzymes in this pathway as can be seen below. The enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase is the first one solely unique to this biosynthetic pathway. It has undergone much scrutiny at the level of enzyme activity since it is regulated by feedback inhibition by pyrimidine nucleotides in numerous species. My laboratory has shown that the regulation of this enzyme does differ according to the DNA homology group to which the species has been assigned. Moreover, my laboratory has demonstrated that regulation of pyrimidine biosynthetic enzyme synthesis in species of Pseudomonas is regulated by pyrimidines which changed the view that pyrimidine biosynthesis was not regulated in pseudomonads. My laboratory has also investigated the regulation of the enzyme aspartate transcarbamoylase in pseudomonads. The regulation of aspartate transcarbamoylase in pseudomonads is different than what has been observed for the Escherichia coli enzyme. It is the goal of this REU project to allow a student to learn how to process cells, prepare cells for assaying and assay the de novo pyrimidine biosynthetic enzymes. This will allow a student to understand the basic principles of biochemistry as it relates to enzymes.
To request a change to this page or to request access to make changes yourself, email helpdesk@tamuc.edu.

